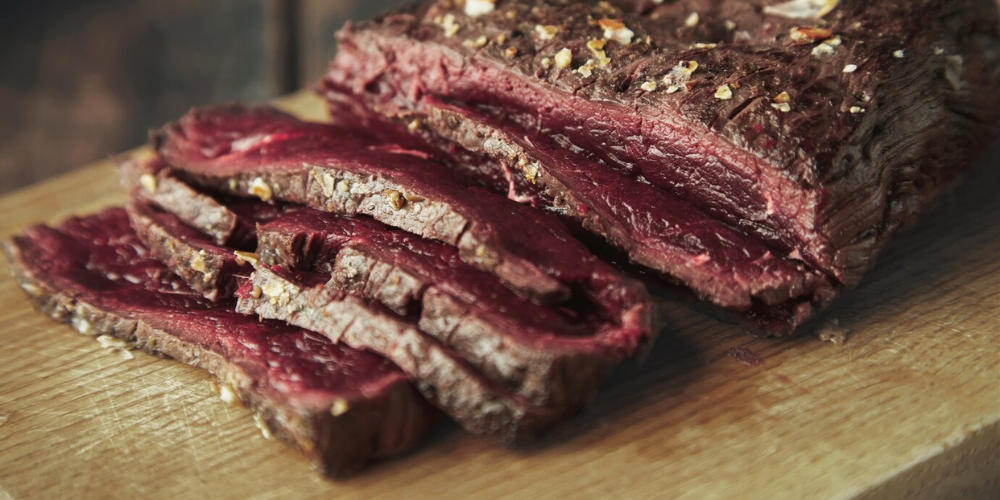

Is Red Meat and Sugar Raising Colorectal Cancer Risk in Young Adults?

Colorectal cancer has long been associated with aging, but a concerning shift is happening—more young adults are being diagnosed with the disease. While genetics play a role in some cases, emerging research suggests that dietary and environmental factors could be a driving force.
A recent study highlights how red meat and sugar consumption may be influencing the rise in colorectal cancer among individuals under 50.
The Impact of Diet on Colorectal Cancer Risk
Metabolites and Their Role in Cancer Development
How Red Meat and Sugar Affect Metabolism
1. Red Meat
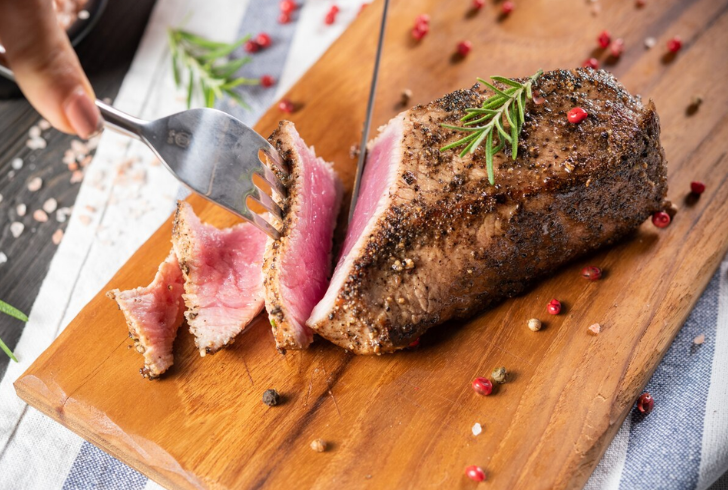

Freepik | jcomp | Consuming red meat is linked to potential inflammation, cancer, and digestive complications.
Processed and unprocessed red meat contain compounds that may contribute to inflammation and increase cancer risk. Cooking red meat at high temperatures can also produce harmful substances that affect the digestive system.
2. Sugar
Diets high in sugar can lead to metabolic imbalances, contributing to obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are linked to colorectal cancer. The body’s response to excessive sugar intake may trigger changes in cellular pathways, increasing the likelihood of tumor development.
The Rising Trend of Colorectal Cancer in Young Adults
Over the past few decades, there has been a noticeable rise in colorectal cancer cases among younger adults. Unlike older individuals, many of these cases are not tied to genetic factors. Researchers believe that environmental influences, particularly dietary habits, may be at play.
A study conducted using samples from colorectal cancer patients revealed significant differences in metabolic pathways between younger and older individuals. The analysis found disruptions in carbohydrate and protein metabolism in younger patients, suggesting that dietary choices early in life could impact cancer risk later on.
What Experts Are Saying
Medical professionals stress the importance of understanding how diet affects colorectal cancer risk. One oncologist involved in the study explained, “Metabolomics allows us to see how diet and environmental exposures influence cancer development, bridging the gap between genetics and lifestyle choices.” Another expert added, “The increase in colorectal cancer among young adults is a major concern. While we cannot pinpoint one single cause, dietary patterns appear to be a significant factor.”
Further research is needed to fully understand the connection, but existing evidence strongly suggests that excessive consumption of red meat and sugar plays a role in early-onset colorectal cancer.
How Diet Can Make a Difference

Freepik | Lower cancer risks and optimized metabolism result from cutting sugary and processed intake.
Making dietary adjustments may help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. Experts recommend the following:
1. Limit Red Meat Intake – Reducing consumption of processed and high-fat red meats can lower the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
2. Reduce Sugar Consumption – Cutting back on sugary drinks and processed foods can help maintain balanced metabolism and reduce cancer-related risks.
3. Increase Fiber Intake – Foods rich in fiber, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, promote gut health and may lower cancer risk.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight – Obesity has been linked to various cancers, including colorectal cancer. A balanced diet and regular physical activity can help manage weight.
The Need for Further Research
While this study provides valuable insights, more research is necessary to confirm the exact mechanisms behind the link between red meat, sugar, and colorectal cancer in younger individuals. Medical advancements may also lead to targeted treatments based on metabolic differences in cancer patients.
With colorectal cancer cases rising among younger adults, understanding dietary influences becomes more critical than ever. By making informed choices and promoting healthier eating habits, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing this serious disease.
More inHealthy Trends
-
`
Deal With Lower Back Pain With These Yoga for Sciatica Exercises
Lower back pain can disrupt daily life, especially when caused by sciatica. This condition occurs when the sacral nerve, located at...
November 29, 2024 -
`
8 Expert Tips for Staying Healthy in the Winter
Staying healthy in the winter requires a proactive approach, as cold weather can challenge immune strength and mental well-being. With a...
November 21, 2024 -
`
Concussion in Children: What Parents Need to Know for Safe Recovery
A concussion in children, especially from contact sports, requires careful attention to symptoms and recovery. A concussion, or mild traumatic brain...
November 15, 2024 -
`
Can Hypochlorous Acid Transform Your Skin Routine and Banish Acne?
Hypochlorous acid is rapidly gaining attention in the skincare world thanks to its potential to fight acne and support clear skin....
November 8, 2024 -
`
How Calisthenics Can Help Improve Your Overall Fitness?
Calisthenics is not a mere workout. It is a fitness revolution. Unlike weightlifting or running, calisthenics uses only your body weight...
November 2, 2024 -
`
10 Must-Have Foods for Kidney Health You Need in Your Diet
Our kidneys are powerhouse organs, working constantly to remove waste, balance fluids, and regulate essential minerals like sodium and potassium. These...
October 26, 2024 -
`
The Les Mills Fitness Festival in Riyadh | An Immersive Fitness Experience
The Les Mills Fitness Festival is coming to Riyadh. It is set to be a fitness experience like no other! On...
October 19, 2024 -
`
How Healthy Are Oats Actually? A Closer Look
Oats have become a staple in many breakfast bowls and snack bars. But are oats healthy? The short answer is yes!...
October 11, 2024 -
`
Here’s How You Can Detox Your Body & Start Afresh
Feeling sluggish, bloated, or mentally foggy? Learning how to detox may be the solution you need to refresh your body and...
October 4, 2024














You must be logged in to post a comment Login